Handling Multiple Files¶
Introduction¶
For a paper or maybe even a short report, it is normally fairy easy to have a single source file (.tex) and an external bibliography (.bib) that it links to.
This source file will tend to be fairly short, even with the sectioning and potential preamble with custom macros defined.
Things get difficult to handle when you come to thinking about writing books, a thesis, or technical documentation for code - your source file will start to bloat in size, and will become unwieldy to use.
What's more; the documents that you find yourself writing will normally share some common notation and conventions, and you don't want to have to go to the hassle of inserting any additional macros or importing commonly used packages each time.
Divide and Conquer¶
When you have to write a long document, the best plan is a divide-and-conquer approach. Rather than writing every chapter (and all your macro definitions) in the original source file; why not instead write each chapter as a separate file, and then link these files together? This is the approach we can going to demonstrate in this lesson; we will show how to link files containing snippets of source code together, and how to get $\LaTeX$ to compile them and produce a single output document.
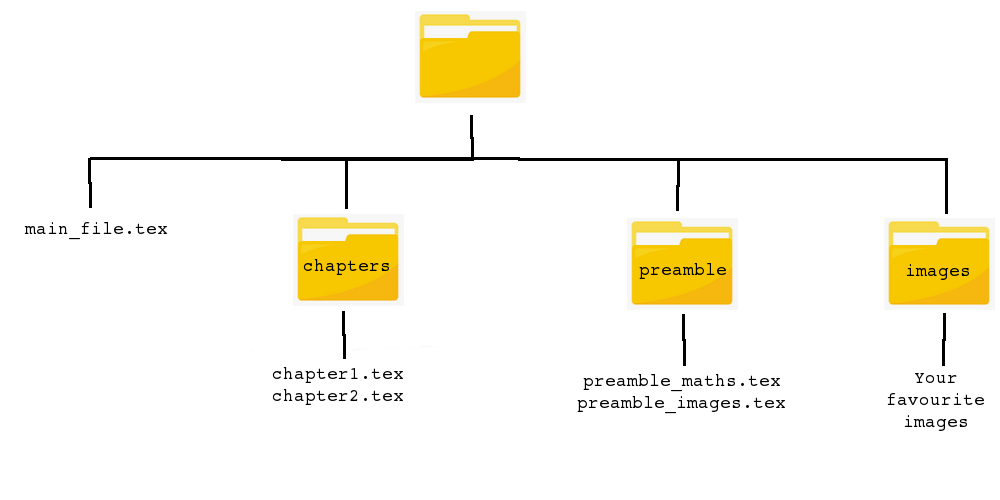
main_file.tex¶
Compile the file main_file.tex using the 3-step $\LaTeX$, BibTeX, $\LaTeX$ technique to ensure that the internal references sort themselves out correctly, and take a look at the output file main_file.pdf.
It (should!) consist of a book containing two short chapters - one just posing a question and showing an image, and the second chapter detailing the answer to the question.
All in all, it seems a fairly standard document.
However if you look at the source code for main_file.tex, you might be surprised to see it's really quite short:
\documentclass[10pt,a4paper]{book}
\input{./preamble/preamble_maths}
\input{./preamble/preamble_images}
\begin{document}
\include{./chapters/chapter1}
\include{./chapters/chapter2}
\end{document}
In actual fact, main_file.tex is simply pulling in $\LaTeX$ syntax from the other 4 .tex files that are scattered thoughout the various folders.
\input and \include¶
You should also notice that there are two commands here that you haven't seen before; \input and \include.
These are the commands that are pulling in information from other .tex files, and dumping them into main_file.tex.
What these commands are actually doing is finding the files they are told to, then effectively "copy and pasting" exactly what's in those files directly into main_file.tex.
This is why, if you look at any of the files in the chapters or preamble folders, they don't have a \documentclass or \begin{document} - it's because that is done inside main_file.tex, and the other files simply hold the content (and syntax) we want to import into our master file.
Before the \begin{document}, we have to use the \input command to pull in files.
After the \begin{document}, you can use either, although \include is normally the best choice.
Both of these commands work in the same way - they take one argument, which is the path to the file you want the content of.
The argument for both of these commands is the path to the file that you want to include, from the path that you have the \input or \include command in.
In this case, our \inputs and \includes are in main_file.tex.
The \input{preamble/preamble_maths} command for example, works from the directory main_file.tex is in, goes into the preamble folder, and extracts the contents of the file preamble_maths.tex that lives there.
The Preamble Files¶
Let's now take a look at the files in the preamble folder.
If you completed the previous lesson on macros, then you'll know that macros are very useful for standardising your notation and formatting.
But a long report or book is going to result in a lot of notation and formatting conventions, and manually typing these out in main_file.tex will make it cumbersome.
You'll also likely start wondering which packages introduce which functions; is it amsmath or amssymb that brings in \mathbb, for example?
You might not need one of these packages after editing, but could still be including it because you haven't realised you're not using any of it's commands.
In addition, you might be writting several reports or papers over the course of your degree/PhD/academic career on similar topics, and will want the same notation throughout.
The ethos behind the preamble folder is that it contains the files that define all our custom macros for these purposes - having one "global" master file that we can import is much easier than typing out everything manually each time, and leaving it in main_file.tex.
You'll notice that preamble_maths contains our custom maths-environment commands, including \bracs from before, alongside some macros for writing some common sets, like that of the natural numbers.
The Chapter Files¶
The files in the chapters folder are written as though they were directly inserted into main_file.tex - this is why you won't find a \documentclass or \begin{document} in them.
You should also realise that we can still use $\LaTeX$ commands that we import from our preamble files:
- We can create a figure in
chapter1.texusinggraphicx, and don't need to give the full path to the image file. Both of these due to the commands inpreamble_images.tex. - We can still use our custom macros that we created using
\newcommand, like those inpreamble_maths.tex- you can see that we use\bracsin a few places, as well as the custom\reicpcommand is.
Armed with this understanding, there isn't a whole lot more to the chapter files - simply begin typing your source code as you normally would!